பாகவதர்
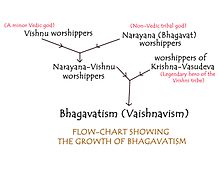
பாகவதர் (Bhagavata) என்ற சொல், இந்து சமயத்தில் குறிப்பாக பக்தி இயக்கத்தின் போது, வைணவ சமயத்தில், பகவான் திருமாலின் மேலான அடியவர்கள், திருமால் மீதான பக்தியை, இசையாலும், நாம ஜெபங்களாலும், நாம சங்கீர்த்தனைகளாலும், உபன்நியாசங்களாலும் திருமாலின் கல்யாண குணங்களையும், அவதார மகிமைகளையும் மக்களிடையே பரப்பியவர்களை பாகவதர்கள் என்பர்.[1][2]
பாகவத மரபு
[தொகு]பக்தி இயக்கத்தின் எழுச்சியால் உருவான பாகவத மரபினர் தங்கள் குடும்ப வருமானத்திற்காக எத்தொழிலும் செய்யாது, உஞ்சவிருத்தியின் மூலம் கிடைக்கும் உணவை மட்டுமே உண்டு, எப்பொழுதும் திருமாலின் நாமத்தையும்; கல்யாண குணங்களையும் இசையுடன் பாடுதல், நாமங்களை ஜெபித்தல், திருமாலின் அவதார மகிமைகளையும், கல்யாண குணங்களையும், குறிப்பாக பாகவத புராணம், இராமாயணம், மகாபாரதம் போன்ற காவியங்களை மக்களிடையே எடுத்துச் சொல்வதன் மூலம் திருமால் பக்தியை மக்களிடையே பரப்புவதே பாகவத மரபினரின் முதன்மைப் பணியாகும். பாகவத மரபு முதலில் மத்திய இந்தியா மற்றும் மேற்கு இந்தியாவில் தோன்றி பின்னர் தென்னிந்தியா மற்றும் கிழக்கிந்தியாவில் நன்கு பரவியது. தற்காலத்தில் அகில உலக கிருஷ்ண பக்தி இயக்கத்தினர் மற்றும் சுவாமிநாராயண் இயக்கத்தின் பாகவதர்கள் உலகெங்கும் கிருஷ்ணர், இராமர் மற்றும் நர நாராயண பக்தியைப் பரப்பினர்.
பாகவதர்களின் மேன்மையை விளக்கும், பாகவதர்களின் கதைகள் அடங்கிய ஸ்ரீமத் பக்த விஜயம் எனும் நூல் பிற்காலத்தில் பிரபலமானது.[3][4]
புகழ் பெற்ற பாகவத மரபினர்
[தொகு]
- துளசிதாசர்
- நாமதேவர்
- ஜெயதேவர்
- தியாகராச சுவாமிகள்
- துக்காராம்
- ஏகநாதர்
- வல்லபாச்சார்யா
- சைதன்யர்
- நிம்பர்க்கர்
- ரவிதாசர்
- இராமாநந்தர்
- வேங்கடரமண பாகவதர்
- நடனகோபாலநாயகி சுவாமிகள்
- அன்னமாச்சாரியார்
- ஊத்துக்காடு வெங்கட சுப்பையர்
இதனையும் காண்க
[தொகு]மேற்கோள்கள்
[தொகு]- ↑ Hastings 2003, ப. 540
- ↑ Beck, G. (2005). "Krishna as Loving Husband of God". Alternative Krishnas: Regional and Vernacular Variations on a Hindu Deity. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண்:978-0-7914-6415-1. http://books.google.com/?id=0SJ73GHSCF8C. பார்த்த நாள்: 28 April 2008. Vishnu was by then assimilated with Narayana
- ↑ பக்த விஜயம்
- ↑ "ஸ்ரீமத் பாண்டுரங்க பக்த விஜயம்". Archived from the original on 2017-04-08. பார்க்கப்பட்ட நாள் 2016-08-12.
மேல் வாசிப்பிற்கு
[தொகு]- Dahmen-Dallapiccola, Anna Libera; Dallapiccola, Anna L. (2002). Dictionary of Hindu lore and legend. London: Thames & Hudson. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண் 0-500-51088-1.
- Hastings, James Rodney (2003) [1908–26]. Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics. Vol. Volume 4 of 24 ( Behistun (continued) to Bunyan.). John A Selbie (2nd edition 1925–1940, reprint 1955 ed.). Edinburgh: Kessinger Publishing, LLC. p. 476. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண் 0-7661-3673-6. பார்க்கப்பட்ட நாள் 3 May 2008.
The encyclopaedia will contain articles on all the religions of the world and on all the great systems of ethics. It will aim at containing articles on every religious belief or custom, and on every ethical movement, every philosophical idea, every moral practice.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - Thompson, Richard, PhD (December 1994). Reflections on the Relation Between Religion and Modern Rationalism. http://content.iskcon.com/icj/1_2/12thompson.html. பார்த்த நாள்: 12 April 2008.
- Gupta, Ravi M. (2004). Caitanya Vaisnava Vedanta: Acintyabhedabheda in Jiva Gosvami's Catursutri tika. University of Oxford.
- Gupta, Ravi M. (2007). Caitanya Vaisnava Vedanta of Jiva Gosvami. Routledge. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண் 0-415-40548-3.
- Ganguli, K.M. (1883–1896). The Mahabharata of Krishna Dwaipayana Vyasa. Kessinger Publishing.
- Ganguli, K.M. (1896). Bhagavad-gita (Chapter V). The Mahabharata, Book 6. Calcutta: Bharata Press.
- Wilson, H.H. (1840). The Vishnu Purana, a System of Hindu Mythology and Tradition: Translated from the Original Sanscrit and Illustrated by Notes Derived Chiefly from Other Puranas. Printed for the Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland.
- Prabhupada, A.C. (1988). Srimad Bhagavatam. Bhaktivedanta Book Trust.
- Kaviraja, K.; Prabhupada, A.C.B.S.; Bhaktivedanta, A.C. (1974). Sri Caitanya-Caritamrta of Krsnadasa Kaviraja. Imprint unknown.
- Goswami, S.D. (1998). The Qualities of Sri Krsna. GNPress. pp. 152 pages. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண் 0-911233-64-4.
- Garuda Pillar of Besnagar, Archaeological Survey of India, Annual Report (1908–1909). Calcutta: Superintendent of Government Printing, 1912, 129.
- Rowland, B., Jr. (1935). "Notes on Ionic Architecture in the East". American Journal of Archaeology 39 (4): 489–496. doi:10.2307/498156.
- Delmonico, N. (2004). "The History of Indic Monotheism And Modern Chaitanya Vaishnavism". The Hare Krishna Movement: the Postcharismatic Fate of a Religious Transplant. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண்:978-0-231-12256-6. http://books.google.com/?id=mBMxPdgrBhoC&pg=PA31&dq=Vaisnava+monotheism. பார்த்த நாள்: 12 April 2008.
- Mahony, W.K. (1987). "Perspectives on Krsna's Various Personalities". History of Religions 26 (3): 333–335. doi:10.1086/463085. https://archive.org/details/sim_history-of-religions_1987-02_26_3/page/333.
- Beck, Guy L., ed. (2005). Alternative Krishnas: Regional and Vernacular Variations on a Hindu Deity. SUNY Press. பன்னாட்டுத் தரப்புத்தக எண் 0-7914-6415-6.
- Vyasanakere, Prabhanjanacharya. Download and Listen to Bhagavata in Kannada. Vyasamadhwa Samshodhana Pratishtana.
- Vyasanakere, Prabhanjanacharya. Download and Listen Shloka by Shloka of Bhagavata and translation in Kannada. Vyasamadhwa Samshodhana Pratishtana.
